Bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery
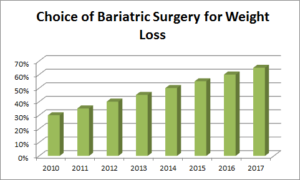
Patients Choosing Bariatric Surgery Growing
Bariatric Surgery (also known as obesity surgery or weight loss surgery) includes a variety of procedures performed on people suffering from Obesity.
Obesity is a life threatening disease as declared by WHO (World Health Organisation) that needs to be treated like any other disease because it triggers over 60 different co-morbidities including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, infertility, sleep apnea etc that are documented to reduce life span of an obese patient by 7- 10 years.
Diet and Exercise should be the first choice of treatment for Obesity patients.
If weight does not reduce or the lost weight quickly bounces back in spite of strict diet and exercise regimen, then Bariatric surgery may be a safe and scientifically proven choice under certain conditions.
Who can undergo Bariatric Surgery?
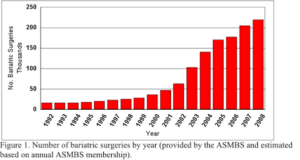
Bariatric Surgery Growth over Years
Not everyone can opt for Bariatric surgery procedures. There are guidelines based on BMI and pre-existence of one or more co-morbid conditions.
ASMBS (American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgeons) has set up a widely followed guideline for bariatric surgery where patient has to meet at least one of the conditions below:
- BMI ≥ 40, or more than 100 pounds (45.3 kilos) overweight. For example, an adult who is 5’11” tall and weighs 132 kilos would have a BMI over 40.
- BMI ≥35 and at least one or more obesity-related co-morbidities such as type II diabetes (T2DM), hypertension, sleep apnea and other respiratory disorders, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, osteoarthritis, lipid abnormalities, gastrointestinal disorders, or heart disease.
- Inability to achieve a healthy weight loss sustained for a period of time with prior weight loss efforts.

A DOSS patient Before & After Bariatric Surgery
Calculate BMI
Who Can Perform Bariatric Surgery?
 Not every center or hospital is qualified to offer this surgery.
Not every center or hospital is qualified to offer this surgery.
The apex medical body National Institutes of Health (NIH) of USA, American College of Surgeons (ACS), American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), International Excellence Federation (IEF) Taiwan etc recommend that Bariatric surgery be performed by a board certified surgeon with specialized experience/training in bariatric and metabolic surgery, and at a center that has a multidisciplinary team of experts for follow-up care.
This may include a nutritionist, an exercise specialist, and a mental health professional such as psychologist. Our center meets all these qualifications and more.
 We are the only center in Pune and Western Maharashtra to be accredited by Taiwan based clinical excellence body International Excellence Federation (IEF). We meet all the above requirements and more.
We are the only center in Pune and Western Maharashtra to be accredited by Taiwan based clinical excellence body International Excellence Federation (IEF). We meet all the above requirements and more.
Types of Bariatric Surgery
Fundamentally, Bariatric procedures work in two ways to reduce and maintain long term excess weight loss.
Either by reducing the size of the stomach to restrict overeating or by resecting and re-routing the small intestine to introduce mal-absorption to reduce excess digestion in some patients that stubbornly put on weight in-spite of eating less and following strict exercise protocol.
Thus the Bariatric procedures fall in two categories: either restrictive or mal-absorptive procedures.
Long-term studies show the Bariatric procedures cause significant long-term loss of weight, complete recovery from diabetes , improvement in cardiovascular risk factors, and a mortality reduction from 40% to 23%.
Bariatric Surgery has five popular and effective procedures:
- Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) which is a restrictive procedure.
- Ru en Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB), a mal-absorptive procedure.
- Mini Gastric Bypass (MGB), a combination of restrictive and mal-absorptive procedure.
- Endoscopic Balloon
- Robotic Bariatric Surgery
Our center has vast experience in performing in all three of these.
Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG)
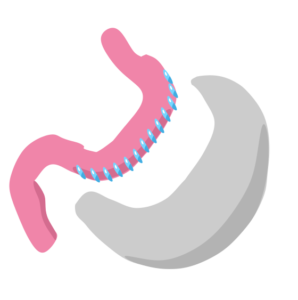 Sleeve gastrectomy is a surgical weight-loss procedure in which the stomach is reduced to about 15% of its original size, by surgically removing a large portion of the stomach along the greater curvature.
Sleeve gastrectomy is a surgical weight-loss procedure in which the stomach is reduced to about 15% of its original size, by surgically removing a large portion of the stomach along the greater curvature.
The result is a sleeve or tube like structure. The procedure permanently reduces the size of the stomach to restrict overeating, although there could be some dilatation of the stomach later on in life. The procedure is best performed laparoscopically and is irreversible.
The actual surgery takes about 50 minutes and at DOSS we perform surgeries as a team to reduce time further.
Weight loss following sleeve gastrectomy results from eating less because of the much smaller stomach. Patient also feels full and satisfied with smaller portions of food due to removal of part of the stomach that produces the hunger hormone (Ghrelin).
What Are the Benefits of Sleeve Gastrectomy?
Patients lose 50-60% of their extra weight within the first 2 years after the surgery. With a complementing exercise routine and healthy diet patients are seen to lose 80-90% of excess weight in one to two years from surgery.
In addition to this weight loss, if you have any of these conditions, they will improve or totally resolve after the surgery:
Type 2 Diabetes
High blood pressure
Sleep apnea
Abnormal lipids/cholesterol
Asthma
Low back pain
Weight-bearing arthritis of the hips, knees, ankles, and feet
Skin fold dermatitis
Urinary stress incontinence
Acid reflux
Metabolic Syndrome
Most importantly, the health benefits gained with Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery can reduce your risk of death by as much as 89% compared to staying morbidly obese.
Contraindications:
There are certain situations in which Sleeve Gastrectomy should not be done:
Lung disease requiring oxygen therapy
Extremely limited mobility
Untreated psychiatric disorders and substance abuse or narcotic dependency
Endocrine disorders such as Cushing’s Syndrome and Prader Willi Syndrome
Psychological instability
Drug or alcohol abuse
Inability to cope with the changes in diet and life modification after surgery
Refusal to be assessed by psychologist or psychiatrist
Complex medical conditions increase the risk of surgery and are considered on a patient-by-patient basis.
Gastric Bypass Surgery
There are two types of Gastric Bypass Surgery: Roux-en-y Gastric Bypass and Mini Gastric Bypass.
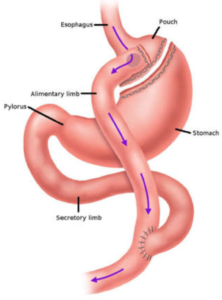 Roux-en-y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)
Roux-en-y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)
RYGB divides stomach into a small upper pouch and a much larger lower “remnant” pouch. And then the small intestine is rearranged to connect to both.
RYGB leads to significant reduction in the functional volume of the stomach, and an altered physiological and physical response to food, thereby deliberately introducing mal-absorption to prevent excessive digestion of the food in obese that causes stubborn weight gain in some people in spite of strict diet and exercise routine.
The laparoscopic or minimally invasive RYGB is performed by introducing a laparoscope, a tiny video camera at the end of a thin long tube, through small abdominal incisions, giving the surgeon a magnified view of the internal organs on a television monitor. The entire operation is performed “inside” the abdomen after gas has been inserted to expand it. Special stapling instruments are used to separate about 5% of the stomach to create a small 10-25 ml Pouch.
The remaining 95% of the stomach (Excluded Stomach) is not removed. It continues to produce digestive juices and some essential factors. The outlet from this newly formed Gastric Pouch is connected to the small intestine (Roux limb) so that food empties directly into the lower portion of the intestine (Small Intestine Common Channel) bypassing the stomach.
Digestive juices produced by the stomach, pancreas, gall bladder and duodenum are directed by the Bilio-Pancreatic Limb back into the common channel in a “Y” shape hookup that gives the technique its name (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass).
The small Gastric Pouch causes patients to feel full sooner and eat less (restriction); bypassing a portion of the intestine means the patient’s body absorbs fewer calories (mal-absorption).
If you try to eat more than 4 parts of food at a meal, you may feel uncomfortable and may regurgitate. This reaction is common, but often is due to inappropriate eating behaviors. You quickly will learn how to eat to avoid discomfort and regurgitation. As you eat less food, your body will stop storing excess calories and it will begin to use its fat energy stores.
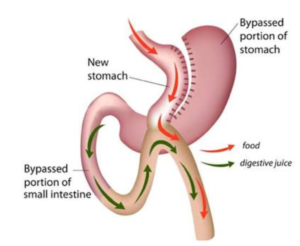 Mini Gastric Bypass
Mini Gastric Bypass
Mini-gastric bypass (MGB) is a promising bariatric procedure. It is also simpler procedure to perform compared to Roux-en-bypass. Tens of thousands of this procedure have been performed throughout the world since 1997.
Mini gastric bypass has only one anastamosis between small pouch of stomach created just after esophagus and second part of small intestine called jejunum compared to Roux-en-y bypass that has two anastamoses.
What are the benefits of Bypass Surgery?
Firstly its reversible. If patients are not satisfied with the surgery, we can totally reverse the surgery.
Secondly, patients report an early sense of fullness and satisfaction that reduces the desire to eat.
Thirdly patients who have gastric bypass generally lose more weight sooner than patients who undergo purely restrictive procedures such as Sleeve Gastrectomy.
Our patient follow-up statistics show that the Gastric Bypass operation performed by DOSS, results in the loss of 60-80% of the extra weight you carry and keep this weight from coming back if you follow our post-operative instructions.
This means if you weigh 150 kilos and should weigh 75 kilos according to your height and body frame, you will lose an average of 45 kgs to 60 kgs with the operation. Some patients lose all their extra weight with complementing diet and exercise routine. While those who do not follow instructions will lose less excess weight and also run the risk of gaining back some weight after 2-3 years of surgery.
In addition to excess weight loss, if you have any of these conditions, they will improve or totally resolve after the surgery:
Type 2 Diabetes
High blood pressure
Sleep apnea
Abnormal lipids/cholesterol
Asthma
Low back pain
Weight-bearing arthritis of the hips, knees, ankles, and feet
Skin fold dermatitis
Urinary stress incontinence
Acid reflux
Metabolic Syndrome
Finally, the health benefits gained with gastric bypass surgery can reduce your risk of death by as much as 89% compared to staying morbidly obese.
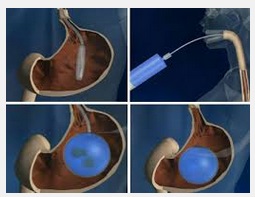 Endoscopic Intra Gastric Balloon:
Endoscopic Intra Gastric Balloon:
This is a non surgical procedure done in a day care setting. A soft silicone balloon filled with saline is placed in stomach and this limits food intake patients full all the time. So overeating is significantly reduced with causes excess weight loss. However, the balloon has to be removed after about six months and there is a risk of lost weight bouncing back if patient is well motivated to stick to the diet and exercise regimen.
Robotic Bariatric Surgery:
We are the only center in Pune and Western Maharashtra offering Robotic Bariatric Surgery. A key advantage of Robotic instrumentation is that they articulate just like human wrist whereas laparoscopic instruments don’t. As a result, complex Hernia surgeries now can be done by keyholes of laparoscopic surgery easily using robotic instruments.
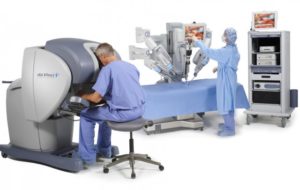 Some people may mistake that Robotic surgery is done by Robots. Actually it is not so. A surgeon controls movements of instruments like a pilot controls the plane. His commands are obeyed by instruments that are much more finer and flexible compared to traditional instruments. As a result superior surgical outcomes are achieved with minimal discomfort to patients.
Some people may mistake that Robotic surgery is done by Robots. Actually it is not so. A surgeon controls movements of instruments like a pilot controls the plane. His commands are obeyed by instruments that are much more finer and flexible compared to traditional instruments. As a result superior surgical outcomes are achieved with minimal discomfort to patients.
Hernia
Hernia
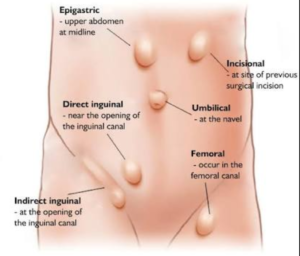
Different Types of Hernia
Hernia is a defect in abdominal wall. When there are weak spots in abdominal muscles or in a connecting tissue called fascia, an organ such as intestine or fatty tissue may push through the defect and a hernia occurs. Surgery is the only scientific treatment available for Hernia. Avoiding or postponing surgery only makes things worse for the patient.
Most common type of Hernia is inguinal (inner groin) which makes up for 96% of all groin hernias and this occurs mostly in men due to their natural weakness in groin area.
Other common types of Hernia are incisional (resulting from an incision of prior surgery or c-section delivery), femoral (outer groin), umbilical (belly button) or hiatal (upper stomach).
Be it any kind of Hernia, concept of repair remains the same. The overhanging abdominal organ or content is first pushed back surgically into the abdomen where it belongs, placing a surgical mesh in most cases to reinforce the area so that Hernia does not recur again and then finally suturing the area for closing the defect in abdominal wall.
Laparoscopic Hernia
A Hernia can be repaired by either conventional open surgery with a big incision of 3 inches to 6 inches or laparoscopic surgery that applies 3-4 tiny incisions of 1/4 inch to 1/2 inch size and a special set of thin instruments used to minimize trauma to the body.
Laparoscopic Hernia repair offers much less postoperative discomfort and pain, reduced recovery time that allows earlier return to full activity, easier repair of a recurrent hernia, the ability to treat bilateral hernias concurrently in the same surgery, the performance of a simultaneous diagnostic laparoscopy, ligation of the hernia sac at the highest possible site, improved cosmetic appearance of abdomen after surgery, and decreased chances of recurrence.
However, its extremely important to choose a well experienced center for Laparoscopic surgery to minimize and avoid complications such as injuries to bowel, bladder, and blood vessels; and potential adhesive complications at mesh placement area.
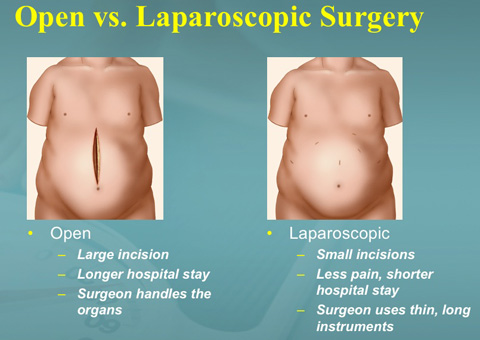
Advantages of Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
3 D Mesh
3 Dimensional Hernia mesh is basically a surgical implant that takes the shape of the body. A 3 D mesh can be placed with open as well as laparoscopic surgery technique. The advantages outweigh the conventional meshes approach in this specific case.

2 D Hernia Mesh

3 D Hernia Mesh
Robotic Hernia Surgery
Robotic Surgery
We are the only center in Pune and Western Maharashtra offering Robotic Hernia Repair. A key advantage of Robotic instrumentation is that they articulate just like human wrist whereas laparoscopic instruments don’t. As a result, complex Hernia surgeries now can be done by keyholes of laparoscopic surgery easily using robotic instruments.
Some people may mistake that Robotic surgery is done by Robots. Actually it is not so. A surgeon controls movements of instruments like a pilot controls the plane. His commonds are obeyed by instruments that are much more finer and flexible compared to traditional instruments. As a result superior surgical outcomes are achieved with minimal discomfort to patients.
Lap GI Surgeries
Lap GI Surgeries
 Gastro Intestinal (GI) surgeries mean procedures on any of the digestive organ starting from esophagus, stomach, gall bladder, liver, pancreas, spleen, small intestine, colon to rectum.
Gastro Intestinal (GI) surgeries mean procedures on any of the digestive organ starting from esophagus, stomach, gall bladder, liver, pancreas, spleen, small intestine, colon to rectum.
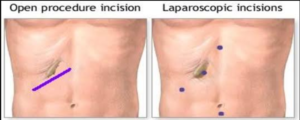
Conventionally GI surgeries were possible only with a large incision of 6 inches to 9 inches on abdomen to make space for the hands of surgeons to reach the diseased part in the abdominal cavity for removal. This approach is called open surgery approach.
Laparoscopic (Also known as Minimally Invasive or Keyhole) approach makes GI surgeries easy on patients although surgeons need very high skills for performing laparoscopic surgeries.
Laparoscopic method helps much less blood loss during surgery, minimum postoperative discomfort and pain, much less chances of infection at incision sites, reduced recovery time that allows earlier return to full activity, improved cosmetic appearance of abdomen after surgery, and decreased chances of herniation at incision sites because laparoscopic incisions are tiny.
Our team has vast experience, high skills, modern equipment and world class protocols in Laparoscopic Colorectal surgery.
Some of the common GI surgeries are explained below and all of them are performed laparoscopically at our center with high success rates and highly satisfied patients.
Foodpipe Tightening or Acidity Surgery (Lap Fundoplication)

Foodpipe tightening Nissen fundoplication
In a healthy individual, food pipe or esophagus has a one-way valve at its bottom. Which means that food you eat is smoothly transported from food pipe to stomach. But when stomach contracts to digest food, the valve closes and does not allow the stomach acids and other digestive juices to flow back into food pipe that would otherwise cause burning sensation. We normally call this condition “Acidity”. Medically it is called GERD or Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease. In most people, medications will solve this problem. If you are not responding to medicines, you may need a simple laparoscopic surgery where upper part of the stomach is wrapped and sutured around the bottom part of food pipe so that the valve functioning is improved and acid reflux is prevented. This procedure is called Funduplication and the Laparoscopic approach makes this surgery minimally invasive.
Food Pipe Loosening Surgery (Lap Cardiomyotomy)

Food pipe loosening surgery or Cardiomytomy
In some people, food pipe has an opposite problem, where the food and liquids do not flow into stomach easily. To resolve this the sphincter muscles forming one-way valve at the bottom of esophagus will have to be cut and relaxed a bit so that we have a nicely funtioning valve.
Until recently, this surgery was performed using an open procedure, either by opening the chest (thoracotomy) or through the abdomen (laparotomy) by large 6inch to 9inch incisions with long and painful recovery. Modern approach is to use minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, which minimize pain, risks and speeds recovery significantly.
Gall Bladder Surgery (Lap Cholecystectomy)
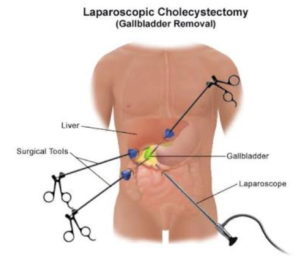
Lap Chole or Keyhole Gall Bladder Surgery
If you experience pain from gall stones that block flow of bile from gall bladder, this surgery may be necessary where gall bladder is removed. There is no health risk to you by removing a diseased gall bladder. Lap cholecystectomy is a very common surgery. When performed laparoscopically using tiny video camara and thin surgical tools sent through four miniature incisions to see inside your abdomen, you can walk home the same day or next day after the procedure with negligible inconvenience. Whereas open gall bladder surgery can be a needless and horrowing experience to patient post operatively due to large cut needed on your abdomen.
Lap Appendix Surgery (Lap Appendectomy)
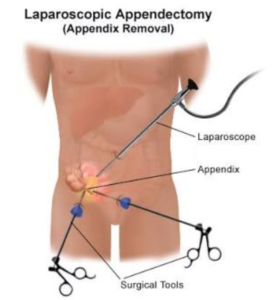
Lap Appendectomy or Lap Appendix Removal
One can do without an appendix with no future health issues. When appendix is inflamed and causing pain at right bottom abdomen, the condition is called appendicitis and the surgery becomes urgent and inevitable. When performed laparoscopically, patients recover much quicker, with little or no pain post operatively at incison and the incisions are barely visible. Laparoscopic approach is also very useful when diagnosis is yet to be established. Surgeons can send the laparoscope (tiny video camara at the tip of a thin cable) through a small slit on abdomen to examine the painful area before taking a decision to conduct the surgery with out causing as much trauma to patient as a large open surgical incision would do.
Lap Colorectal Surgery (For Colon and Rectum)
Colorectal surgery deals with disorders of colon, rectum and anus that can not be treated with medicines alone.
There are many conditions that may be bettered with Colorectal Surgery such as:
- Inflammation of veins in rectum or anus (piles),
- Painful or inflammed cracks or tears in anus (fissures)
- Severe constipation
- No control over passing motion
- Collapse of rectal walls and bulging of rectum out of anus
- Cancer of Colon or Rectum
- Injuries to Anus or Rectum
In recent times, the laparoscopic method of colorectal surgery has seen a surge of popularity, due to its lower risks, decreased recovery time, and smaller, more precise incisions achieved by using laparoscopic instruments.
Minimally Invasive Surgery for Piles (MIPH)
 Piles is one of the most common conditions that bother people with bleeding or/ and painful anus due to swollen veins. Even today, piles is treated at most centers with open technique that has a very long and painful post operative recovery experience. Most patients share that if they knew post operative period would be so painful, they would have rather lived with swollen piles.
Piles is one of the most common conditions that bother people with bleeding or/ and painful anus due to swollen veins. Even today, piles is treated at most centers with open technique that has a very long and painful post operative recovery experience. Most patients share that if they knew post operative period would be so painful, they would have rather lived with swollen piles.
This is totally needless journey. With the help of a surgical stapler and minimally invasive technique, this surgery can be made virtually painless and patients walking home with in a day of surgery with a smile on their face and return to normal routine shortly thereafter.
We are one of the few Centers of Excellence in MIPH (Minimally Invasive Procedure for Hemmorhoids) offering this technique in Pune and Maharshtra.
SILS
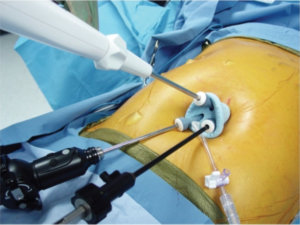
SILS Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery
Single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS) is a very exciting new modality in the field of minimal access surgery which works for further reducing the scars of standard laparoscopy and towards scarless surgery.
SILS is accomplished through a single 20 mm incision in the navel (umbilicus or belly button), or minimizing the scarring associated with the multiple points of entry used during traditional laparoscopic surgery or a large scar of open surgery.
Our Center is equipped with special SILS instrumentation and cutting edge experience to offer many GI surgeries with SILS approach.


 +919011100010
+919011100010 